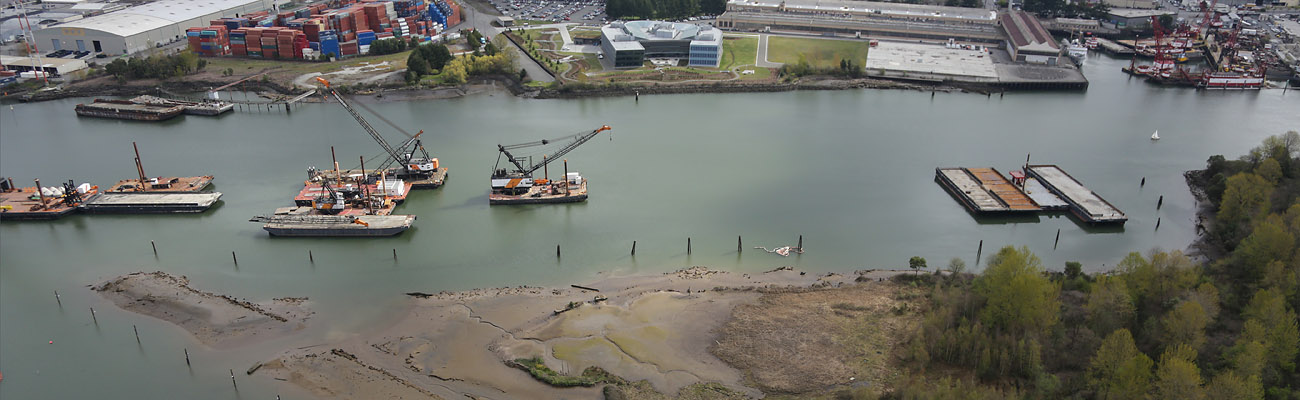
The cleanup is a several hundred-million-dollar effort that takes time and needs to be done right. Once complete, the cleanup of contaminated sediment and pollution source control is anticipated to reduce over 90 percent of the waterway’s PCB sediment contamination. Our scientists are gathering data about the contamination and our engineers will be using this data to ensure the design meets EPA’s cleanup plan requirements.
We are planning ahead for cleanup construction | Cleanup design for the Lower Duwamish Waterway | LDWG Statement on the EPA’s Updated cPAH Standard | Controlling Sources of Contamination
We are planning ahead for cleanup construction
EPA and LDWG are anticipated to begin cleanup construction of the Lower Duwamish Waterway in late 2024.
Construction activities for the sediment cleanup will begin in the upper reach (the southernmost two miles of the Superfund site, between Duwamish Waterway Park and the South 102nd Street bridge) and will continue towards the south end of Harbor Island over the next decade.
We will use a few methods to clean up the waterway sediment, including dredging, capping, natural and enhanced recovery processes. Learn more about how we clean up the river.
Information about the contractor’s planned construction schedule, work areas, and haul routes will be made available to the public as soon as plans are finalized.

Updated Community Outreach and Communications Plan
The Lower Duwamish Waterway Group has updated its cleanup construction Community Outreach and Communications Plan (COCP). The plan details community priorities and how LDWG plans to communicate with the public during cleanup construction in the upper reach. The plan has been recently updated and informed by public input gathered during engagement in 2023.
Estamos planificando la construcción de limpieza en Lower Duwamish Waterway.
យើងគ្រោងនឹងសាងសង់សំណង់រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធសម្អាតនៅក្នុងផ្លូវទឹក Duwamish ផ្នែកខាងក្រោម។
Chúng tôi đang lên kế hoạch cho công trình dọn dẹp ở Lower Duwamish Waterway.
If you’d like to reach out to our team, please contact us at ngraves@stephersonassociates.com.
Cleanup design for the Lower Duwamish Waterway
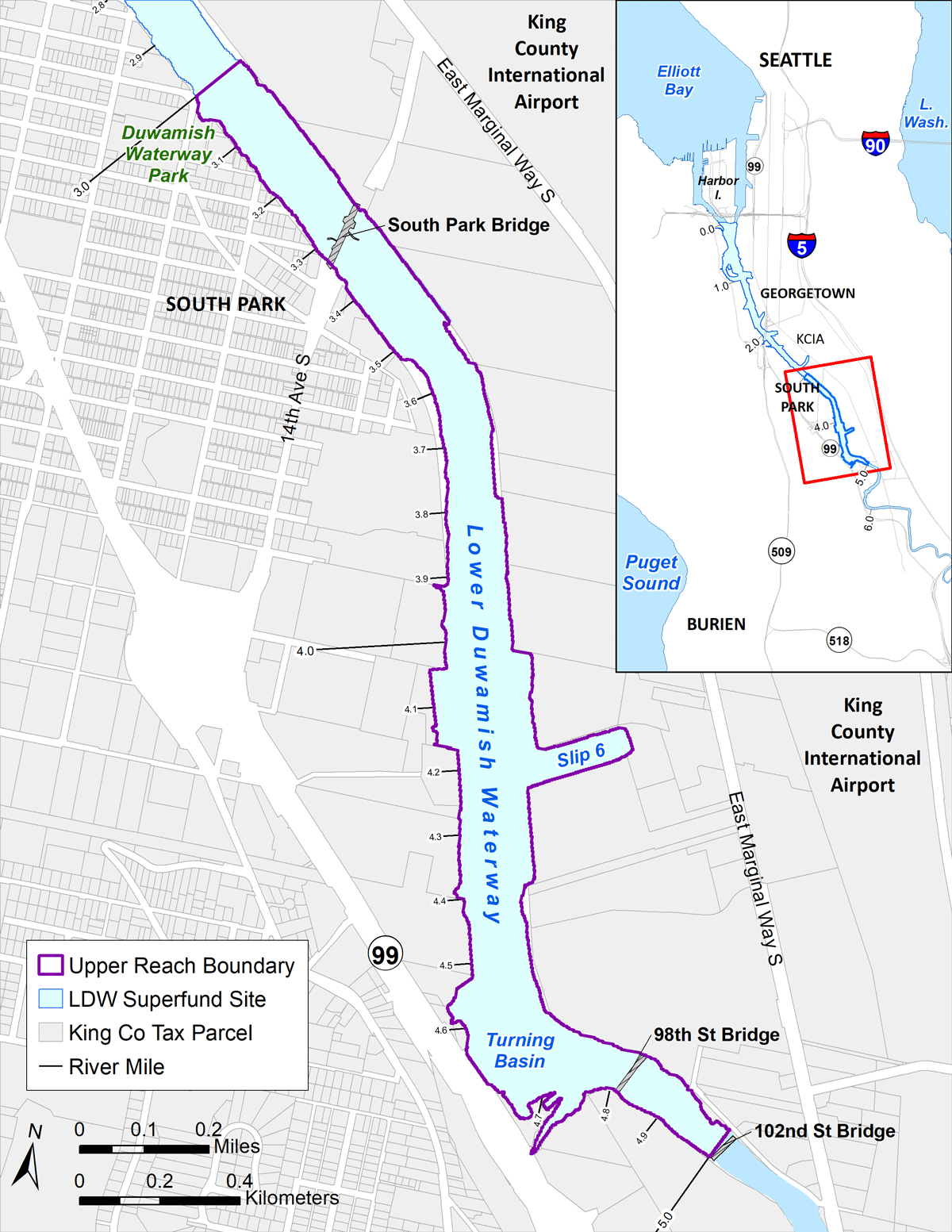
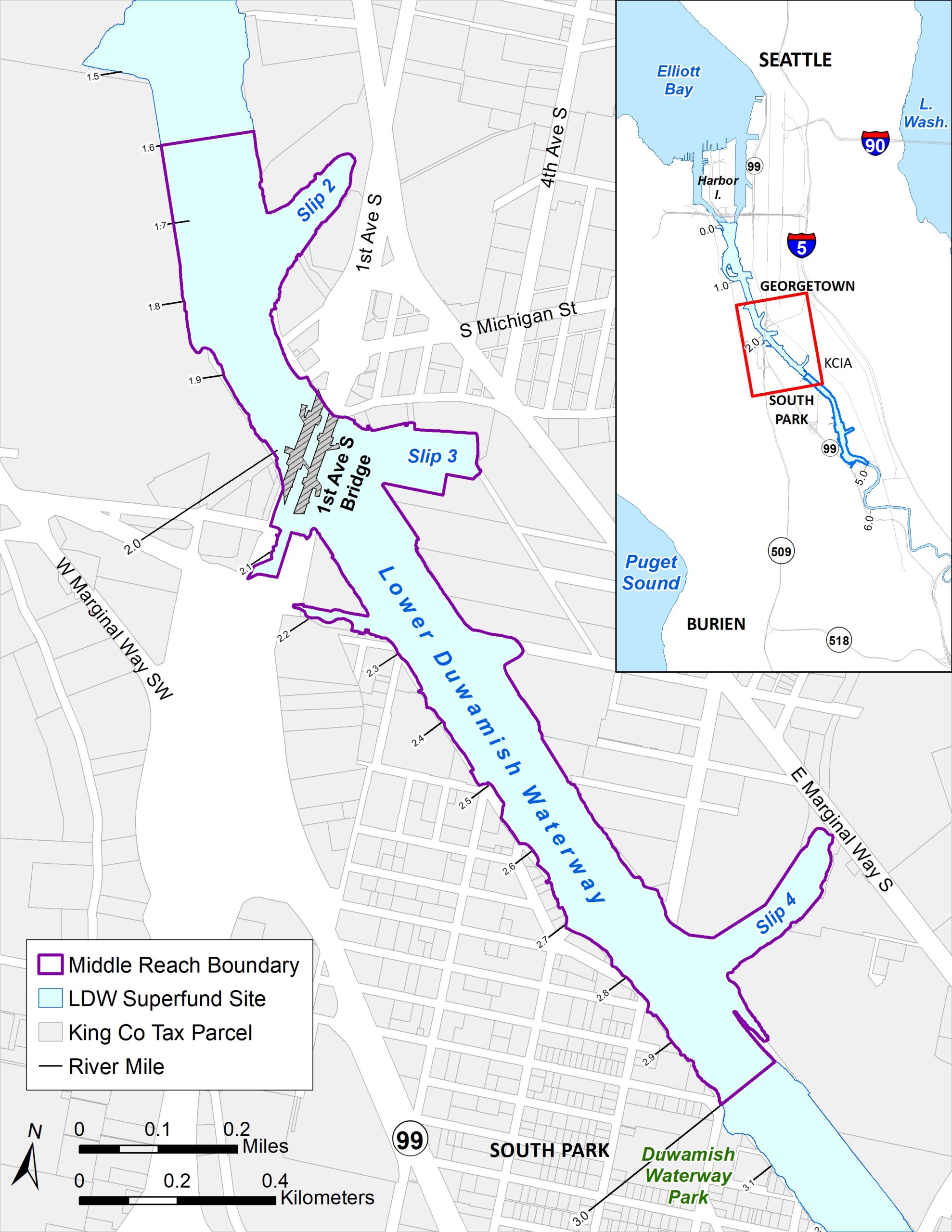
The Lower Duwamish Waterway has been divided into three segments to help implement EPA’s cleanup plan. We call these the upper, middle, and lower reaches. Each section will have its own design and cleanup schedule. Cleanup will begin upstream (south) in the upper reach and move downstream. LDWG is currently designing the cleanups of the upper and middle reaches in support of the EPA-led cleanup plan.
The first step in the design process is to conduct pre-design investigations – in this step, scientists and engineers gather more data about contamination and site conditions in the Lower Duwamish Waterway. Engineers use these data to define which areas need cleanup and decide which cleanup technologies can be used to meet EPA’s cleanup plan requirements in specific locations.
The design goes through three stages before it is finalized: 30%, 60%, and 90%. Each stage provides more information and detail about the design. EPA oversees all steps of the design process and will lead public involvement and engagement through their Roundtable and Stakeholder meetings during the pre-design and design phases to set the final cleanup design.
A Seat at the Table
EPA has convened a “Roundtable” to help affected communities and local agencies work together to mitigate the impacts of cleanup. The Roundtable brings together governments (federal, tribal, state, and local) and other stakeholders (e.g., residents, businesses, industries, labor, neighborhood groups, waterway users, fishers, and others) to share information and make recommendations during the design and implementation of the cleanup plan.
Upper Reach Cleanup Design
In 2020 and 2021, scientists and engineers completed two phases of pre-design investigation work for the upper reach. LDWG completed the 30% Remedial Design in 2022 and in February 2023, submitted the 60% design to EPA. In December 2022, we collected additional investigation samples and we used that data to inform our 90% Remedial Design. We submitted 90% Remedial Design to EPA in July 2023 and completed the final design for the cleanup in January 2024. Remedial design for the upper reach cleanup is now complete and our next phase is to prepare for cleanup construction. LDWG will hire a construction contractor this spring and expect to begin cleanup in the fall. We will provide information about construction in the summer.
Middle Reach Cleanup Design
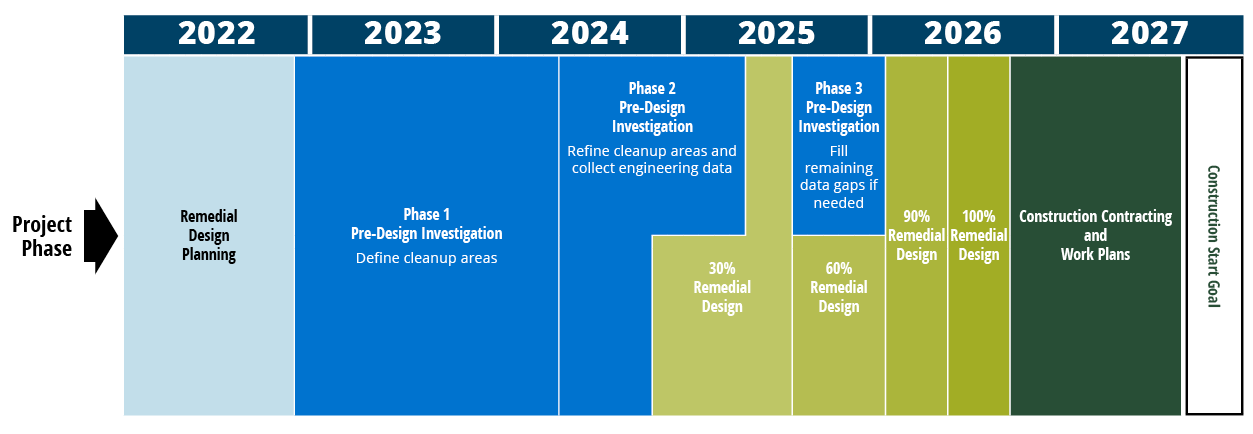
The design process for the middle reach of the Lower Duwamish Waterway is underway. LDWG began collecting sediment samples as part of pre-design investigation work in December 2022. The pre-design investigation work will continue through 2024. We expect to finish the cleanup design for the middle reach in 2026.
Cleanup Construction Schedule for the First Two Reaches
Cleanup construction in the upper and middle reaches of the Lower Duwamish River are expected to begin in late 2024 and late 2027, respectively.
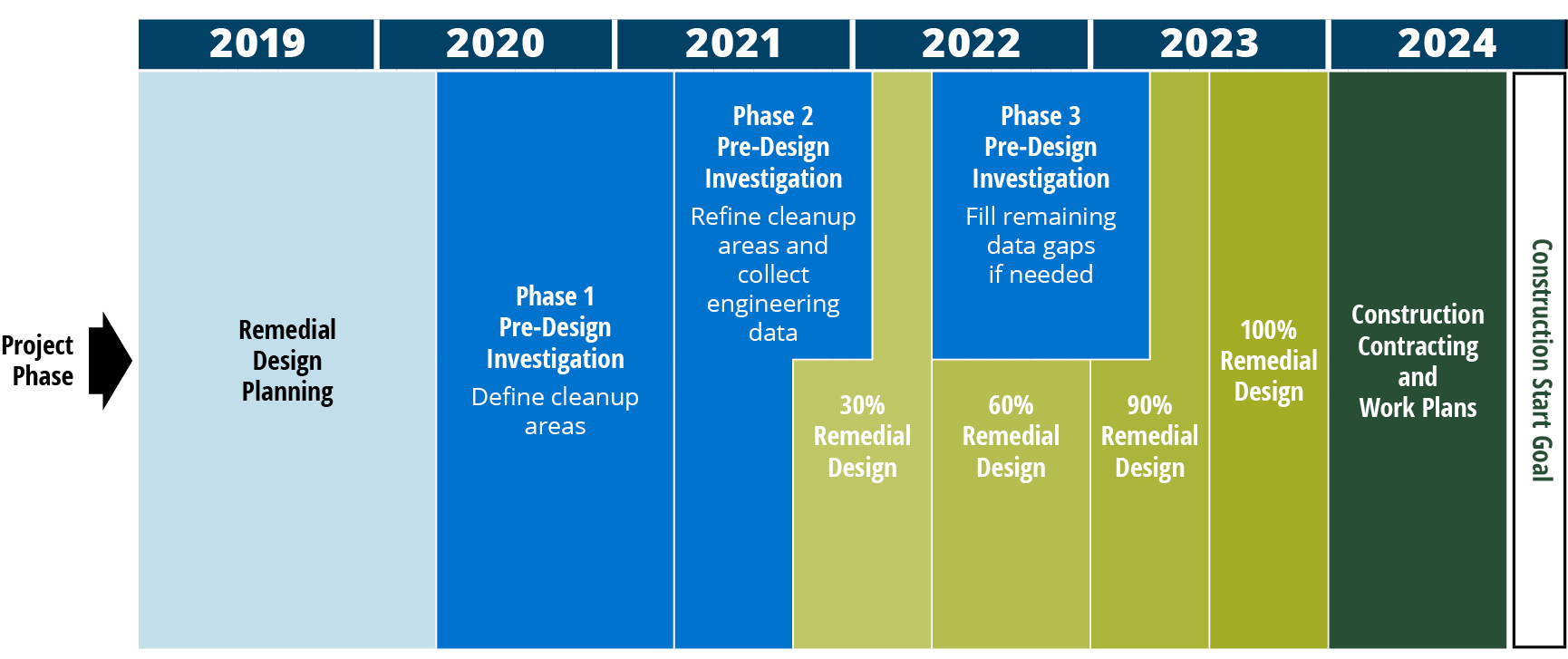
Upper Reach Remedial Design Timeline
Timeline graphic below shows:
- Remedial design planning—January 2019 through Quarter 1 2020
- Three phases of predesign investigation:
- Phase 1: Define cleanup areas—Quarter 2 2020 through Quarter 1 2021
- Phase 2: Refine cleanup areas and collect engineering data—Quarter 2 2021 through early 2022
- Phase 3: Fill remaining data gaps if needed—Quarter 2 2022 through Quarter 1 2023
- Four phases of remedial design:
- 30%—Quarter 4 2021 through Quarter 1 2022
- 60%—Quarter 2 2022 through Quarter 4 2022
- 90%— Quarter 1 2023 through Quarter 2 2023
- 100%— Quarter 3 2023 through Quarter 4 2023
- Construction contracting and work plans— Quarter 1 2024 through Quarter 3 2024
- Construction start goal—Quarter 4 2024
Middle Reach Remedial Design Timeline
Summer 2020, LDWG and its contractors collected samples of sediment to test for contaminants of concern. This will help with the remedial design.
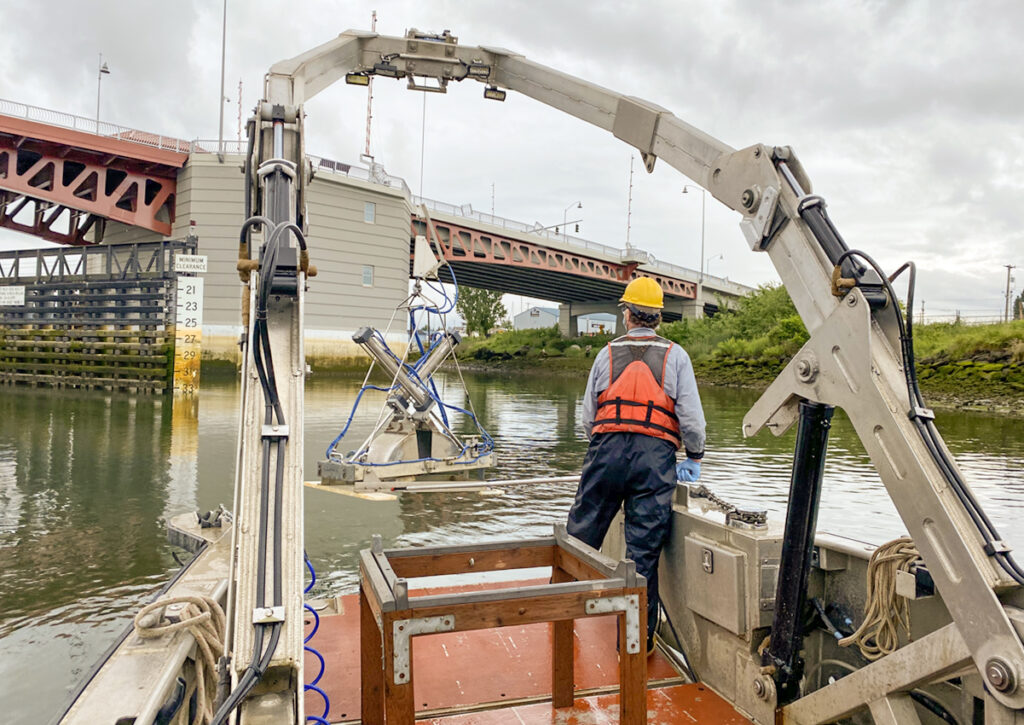

Phase 1: Crews collect a “grab sample” from the Upper Reach of the Lower Duwamish. Photo: Windward Environmental LLC

Phase 1: Example of “grab sample” collected in June 2020. Photo: Windward Environmental LLC
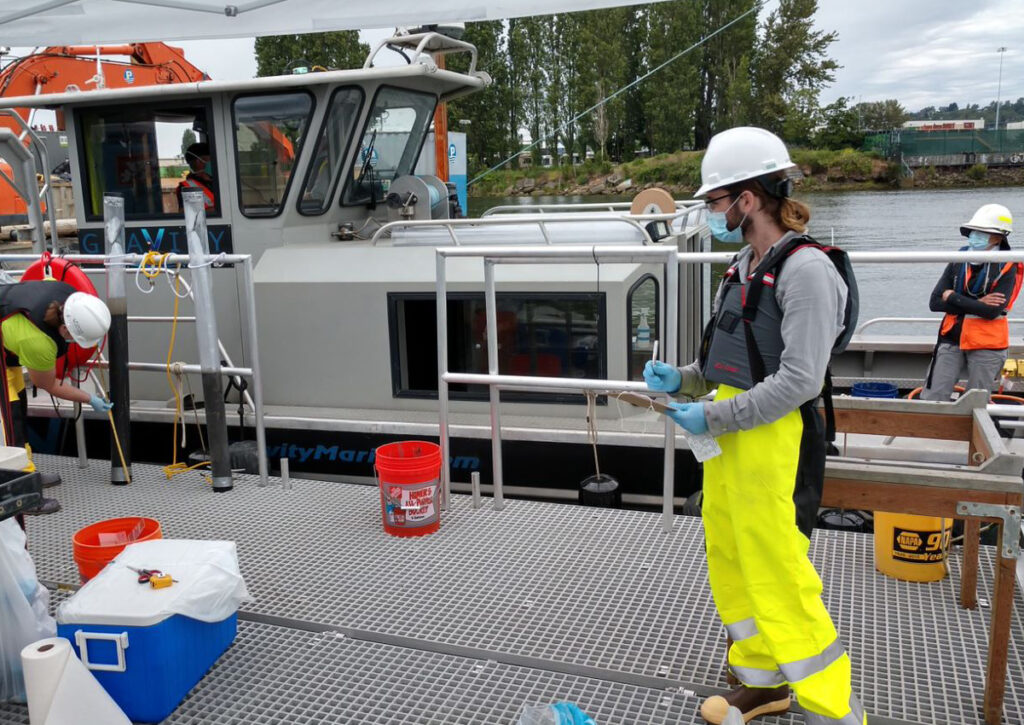

Phase 1: Sample transfer of Lower Duwamish Upper Reach. Photo: Windward Environmental LLC
LDWG Statement on the EPA’s Updated cPAH Standard
Lower Duwamish Waterway Group will voluntarily include additional cleanup actions for the areas where cPAHs are above the original remedial action level in the design for the upper and middle thirds of the waterway. Learn more.
Controlling Sources of Contamination
LDWG partners with EPA and Ecology to keep new and ongoing sources of pollution out of the river.
Contaminants in soil and groundwater on sites around the river can find their way into the river through storm runoff, spills and leaks, industrial discharge, erosion and leaching, and other pathways. Ecology is leading efforts to control sources of contamination from areas upland of the waterway, and EPA is leading efforts to clean up the river sediments. The long-term goal is to minimize re-contamination of the river sediment and restore the river’s water quality.
LDWG partners have helped hundreds of individual businesses and property owners address problems with hazardous materials, industrial wastewater, stormwater, spill containment, and leaking pipes. LDWG partners are also working with agencies to improve the health of the Green/Duwamish watershed, restore natural resources, and further protect fish and wildlife habitat. King County and the City of Seattle are working toward improved water quality with large investments in controlling combined sewer overflows and improving stormwater quality.